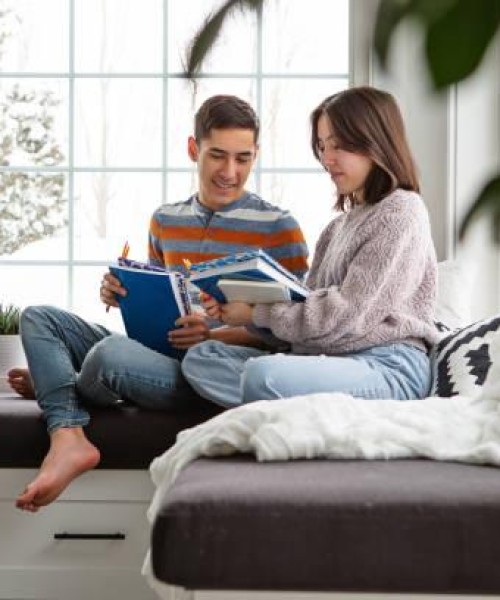
发展是儿童如何和为什么学习的一个重要方面。儿童在成年前经历几个阶段。有生长在儿童学习某些事物的四个阶段:婴儿期(出生至2岁),儿童早期(年龄从3到8),儿童(年龄9至12),青少年(年龄13至18)(博根,W &诺尔曼,E.)。教师要有效地教和理解学生,需要识别发展行为是必要的。青春期是一个更复杂的思维过程的开始。由于这个年龄组包括那些从十三岁到十八岁,在这个发展阶段的青少年经历了各种行为的变化。青少年评价教科书中提到,在认知发展过程中,“思维在青春期发生质的变化。青少年可以更快和更有效地比孩子”(冈比纳,2003,27页)。典型的认知行为,青少年遇到的是:开发先进的推理能力,发展抽象思维能力,发展思维能力(中篇小说,R.)。高级推理技巧包括回答问题:“如果怎么样?”这个技巧包括思考多种选择和可能性。使用更多的假设和逻辑思维技能来处理信息。抽象思维是对不实际存在的事物的思考。这种思维技巧的主要例子是宗教、信仰或信任。思维能力的发展是一个被称为元认知的过程。正如Webster的词典所定义的,元认知是“对自己的学习或思考过程的认识或分析”,这种思维策略可以用来改善学习,这种发展策略的一个例子就是创造记忆装置。认知发展的变化可以影响青少年在一些方面。其中一个影响就是青少年表现出自我意识的提高。青少年倾向于相信每个人都关心他们的想法和行为,因为他们是。青少年也倾向于相信,没有人曾经历过同样的感觉或情绪,因为他们有。这句话中提到了“戏剧女王”这个杜撰的短语。在青少年时期,经常听到的一句话是“你永远不会明白”或“你毁了我的生活”,另一个典型的认知行为在青春期青年是“它不能发生在我身上”或“我无敌”的综合征。十几岁的青少年经常使用这种信念,使风险,如饮酒和驾驶,吸烟,或其他有害的和轻率的行为决定,而不考虑后果。认知行为,如过度取向的倾向,并表现出“正义”的方向也很有青少年发展。一个以原因为导向的行为的例子将是一个十几岁的青少年阅读动物虐待后成为素食主义者。司法导向行为是青少年指出成人话语及其行为缺陷的倾向。十几岁的年轻人可能会对父母说:“但是你让乔尼(哥哥)大二的时候去参加舞会”,他们看到的错误和观点很少,在黑人和白人中看到的更多,而不是灰色的。
澳洲昆士兰论文代写:为什么学习
Development is an important aspect to how and why children learn. Children pass through several stages before becoming adults. There are four stages of growth where children learn certain things: infancy (birth to age two), early childhood (ages 3 to 8), later childhood (ages 9 to 12), and adolescence (ages 13 to 18) (Borgen, W. & Norman, E.). For teachers to effectively teach and understand students, the need to identify developmental behavior is a necessity. Adolescence is the beginning of a more complex thinking process. Since this age group encompasses those from the ages of thirteen to eighteen, teens in this developmental phase experience a variety of behavioral changes. The Adolescent Assessment textbook mentions that in cognitive development, "thinking changes both quantitatively and qualitatively during adolescence. Adolescents can think faster and more efficiently than children" (Gumbiner, 2003, p.27). Typical cognitive behaviors that adolescent youth encounter are: developing advanced reasoning skills, developing abstract thinking skills, and developing the ability to think about thinking (Novella, R.). Advanced reasoning skills involve answering the question, "what if?" This skill includes thinking about multiple options and possibilities. The use of more hypothetical and logical thinking skills are used to process information. Abstract thinking is the use of thinking about things that do not actually exist. Prime examples of this type of thinking skill would be religion, faith, or trust. The development of the ability to think about thinking is a process known as meta-cognition. As defined by Webster's dictionary, meta-cognition is "the awareness or analysis of one's own learning or thinking process." This thinking strategy can be used to improve learning, and an example of this development strategy would be creating mnemonic devices. Cognitive development changes can affect teens in a number of ways. One affect is that teens demonstrate a heightened level of self consciousness. Teens tend to believe that everyone is as concerned with their thoughts and behaviors as they are. Teens also tend to believe that no one has ever experienced the same feelings or emotions as they have. The coined phrase "drama queen" comes to mind in regard to this statement. In adolescent youth, often heard phrases are, "You'll never understand," or "You have ruined my life." Another typical cognitive behavior in the adolescent youth is the, "It can't happen to me" or the, "I'm invincible" syndrome. Teens often use this belief to make risks like drinking and driving, smoking, or other harmful and thoughtless behavioral decisions, without thinking of the consequences. Cognitive behaviors such as the tendency to become overly cause-oriented and to exhibit a "justice" orientation are also very present in adolescent development. An example of cause-oriented behavior would be a teen becoming vegetarian after reading about cruelty to animals. Justice oriented behavior is the tendency of teens to point out flaws between adults' words and their actions. Teens may confront their parents by saying something like, "But you let Johnny (big brother) go to the prom when he was a sophomore." They see little room for error and view points are seen more in black and white, rather than gray.